Leading the way in supporting customers by providing Infrared know-how, affordable sensors, cores and cameras.
Xenics, part of Exosens, is one of the leading suppliers of infrared solutions. Established in Belgium in 2000, Xenics is a renowned designer and manufacturer of infrared sensors, cores and cameras. It was founded as a commercial spin-off of IMEC targeting initially the development of SWIR InGaAs imaging detectors and cameras.
Xenics is committed to expanding its capabilities in advanced imaging, offering Short Wave InfraRed (SWIR) and uncooled Long Wave InfraRed (LWIR) spectra solutions across multiple markets and applications. The implementations benefiting from IR extended vision capabilities in invisible bands enable energy savings, carbon emission reduction, food quality improvement, waste recycling optimization, Green House effect gas detection, world’s security and safety enhancement and a lot more…

Xenics is a designer and manufacturer of infrared sensors, cores and cameras that deliver unparalleled Electro-Optical performance and functionalities.

Solutions for advanced imaging
The Xenics Brand specializes in designing and marketing infrared sensors, cores and cameras that deliver unparalleled Electro-Optical performance and functionalities. Xenics offers a broad, comprehensive and affordable portfolio of line-scan and 2-D area-scan products in the VisNIR and SWIR bands, as well as 2-D uncooled imagers in LWIR. Above its technology and product offerings, Xenics will support your volume requirements leveraging investments in its own European sensor and camera production facility and world class supply chain. Beyond providing exceptional products, Xenics is committed to sharing its extensive knowledge of infrared technology with partners and exploring new and exciting infrared applications and business opportunities.
The Xenics Story
Xenics was established in Belgium in 2000 as a designer and manufacturer of infrared sensors, cores and cameras. As a commercial spin-off from IMEC, Xenics specialises in the development of SWIR InGaAs imaging detectors and cameras. As Xenics continued to grow it opened several successful subsidiaries in Singapore (2008), Boston (2010) and Moscow (2011). Today, Xenics part of Exosens, is aiming to diversify its expertise in advanced imaging through SWIR imagers and LWIR range for various markets.


Use cases
Discover Xenics' application articles in our resource center. These technical documents serve as a valuable resource for Xenics product users, offering detailed information on product usage, technical specifications, troubleshooting tips, and more.
Xenics' application articles cover a wide range of topics, including:
- Installation and configuration of products
- Utilization of product features
- Resolution of common issues
- Application examples
Technologies
See all
Infrared technology
Combining the strengths of both Xenics and Telops technologies in the field of infrared imaging and camera systems lead to innovative and powerful solutions.
Shortwave Infrared technology
Shortwave Infrared (SWIR) technology has emerged as a powerful imaging tool, offering unique capabilities that complement Longwave Infrared (LWIR) and Midwave Infrared (MWIR) systems.

Longwave Infrared technology
For decades, infrared cameras utilizing Longwave Infrared (LWIR) and Midwave Infrared (MWIR) sensors have been a staple in military applications for detecting human activity.
Products 17
See all exosens products
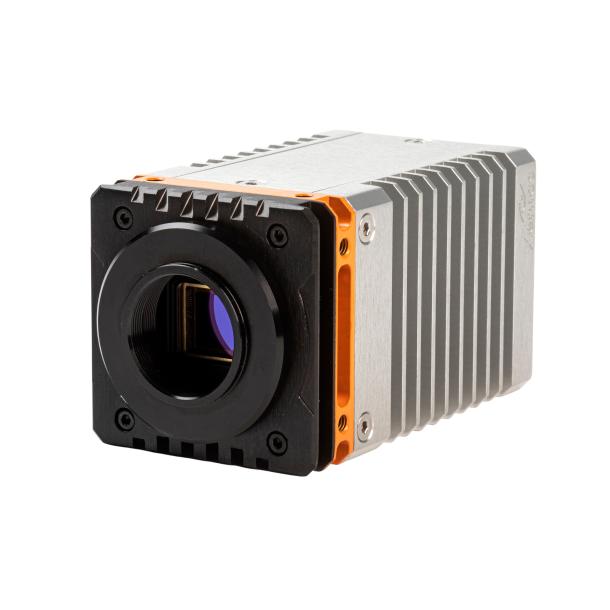
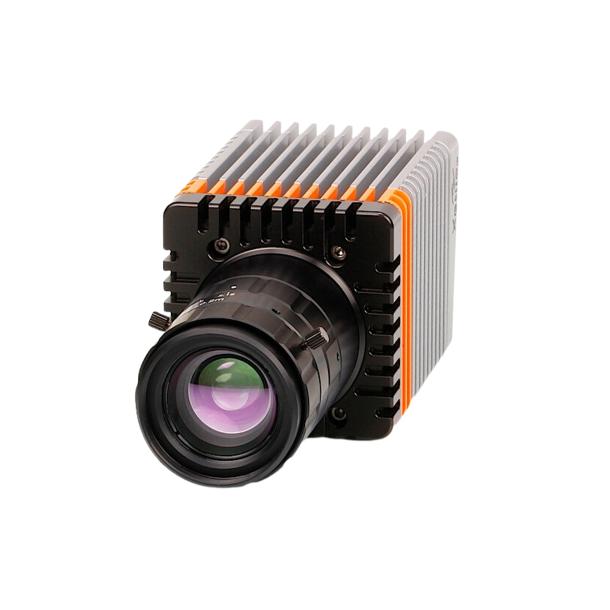
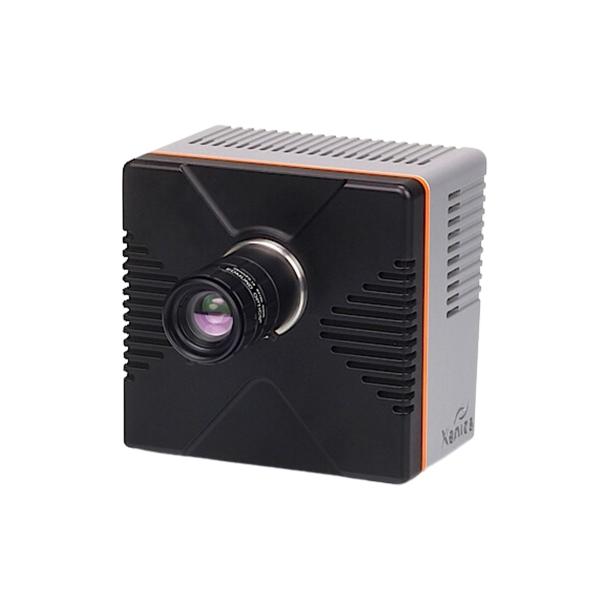
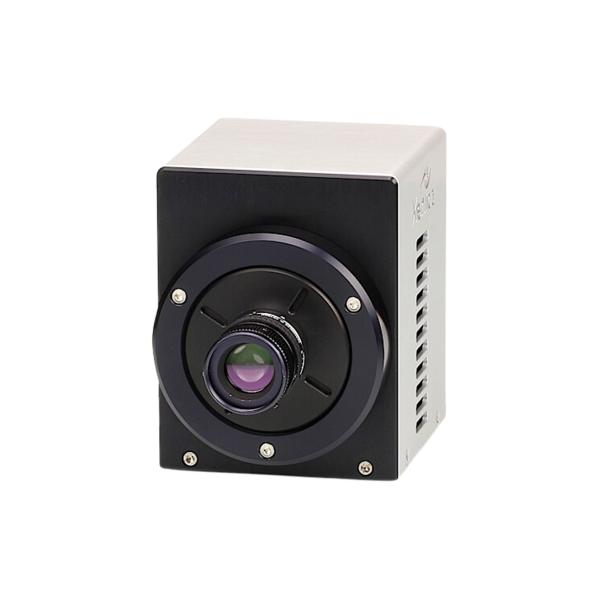
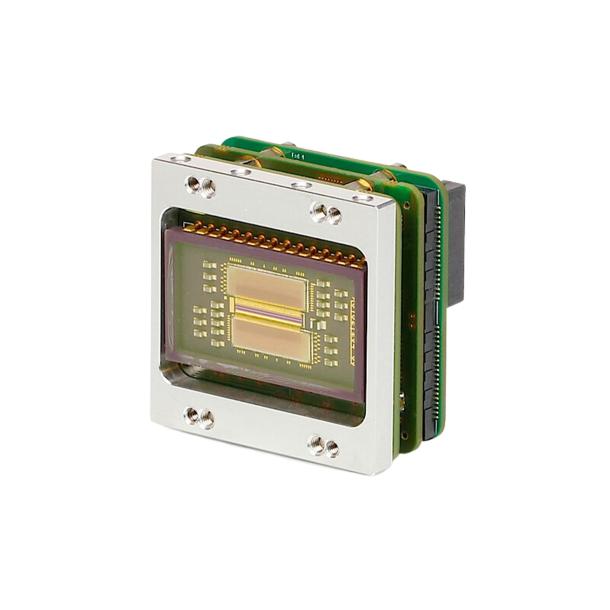
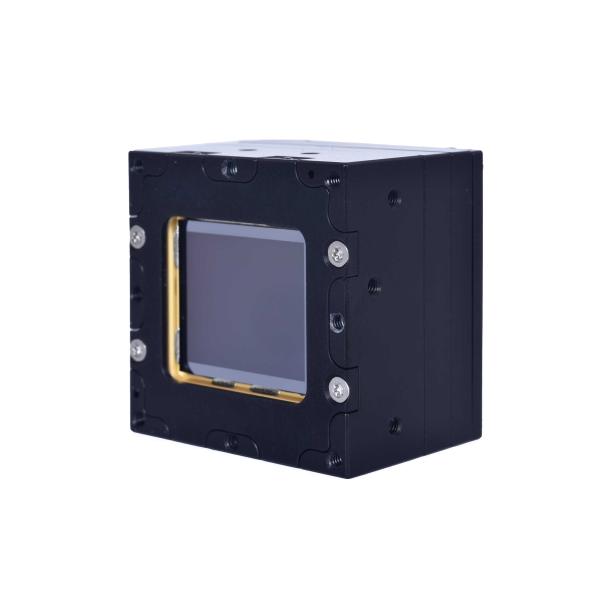
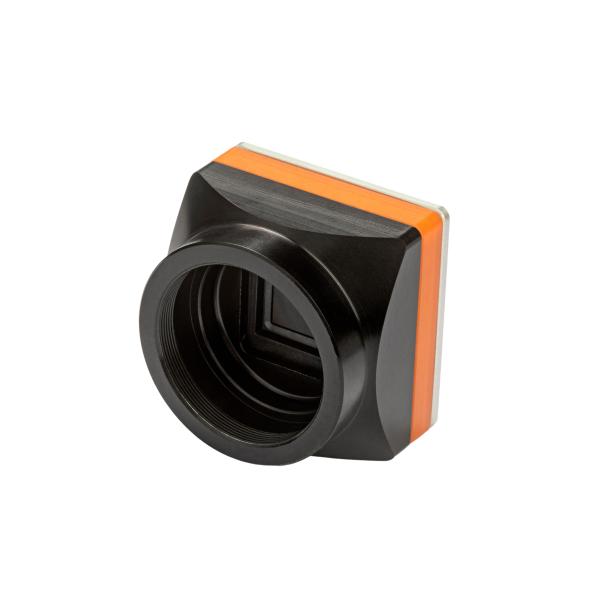
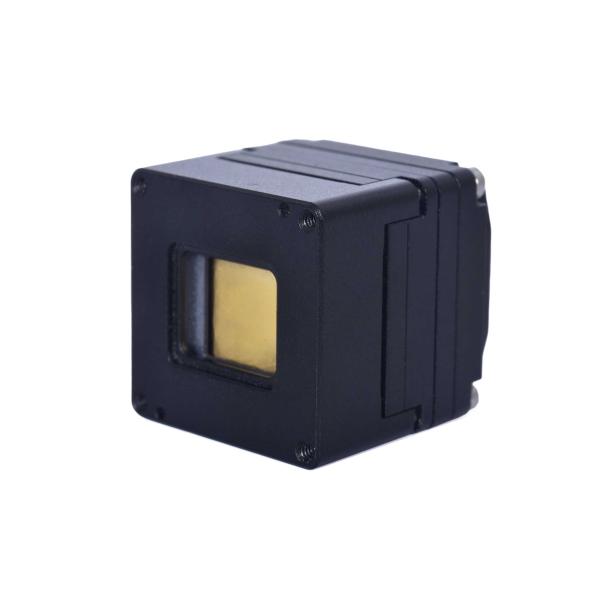
































What's new in Xenics?
See all
KINTEX Exhibition Center Ⅱ.
FROM Sep 25th 2024 TO Sep 28th 2024
DX KOREA 2024
Visit Exosens at DX KOREA 2024 from September 25 to 28 in KINTEX Exhibition Center Ⅱ, Korea

Shanghai New International Expo Centre.
FROM Jul 08th 2024 TO Jul 10th 2024
Vision China 2024
Visit Exosens at Vision China 2024 from July 8 to 10 in Shanghai New International Expo Centre, China

Paris Nord Villepinte exhibition centre.
FROM Jun 17th 2024 TO Jun 21st 2024
Eurosatory 2024
Visit Exosens at Eurosatory 2024 from June 17 to 21 in Paris Nord Villepinte exhibition centre, France


